Virtualization in IT is not easy to understand. What is a virtual machine and why should I use one? Let's try to understand.
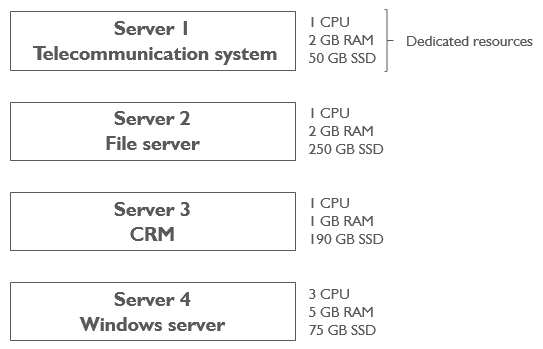
Companies use different IT programs and services. A medium size company could have:
- a telecommunication system (to make and receive calls);
- a file server (to save all kinds of documents such as invoices, offers, etc.);
- a customer relationship management system (CRM);
- a windows server for other applications.
If all four services ran on the same computer (or server) the same problems that we often encounter on our own PC would arise: if I start a program that needs lots of resources, all other programs are slowed down. Sometimes, my computer freezes if I have too many programs opened at the same time. A company cannot allow itself to have its services frozen.
In order to make sure that each program can run well and have enough resources available, we can install them on different servers. In my example, the company needs four different servers:
With four different well chosen servers, I can be sure that each program has enough resources to work properly and that those resources are not shared. Each program is independent from the others and this offers a few advantages:
- If one server crashes, the others keep running as if nothing had happened;
- If I need to make an update on my windows server, the others can keep working;
- if one server has a virus, it does not spread to the others;
Using a dedicated machine for a specific program is an easy way to split the resources and to allocate enough for each program. However, in most cases, using a whole server for only one application is oversized and the initial investment as well as the running costs are much too high. There are other cons to using one server per program:
- Maintenance on 4 different servers is more complicated than on only one;
- Redundancy (automatic hardware failover) is harder and more expensive to achieve;
- Backups are complicated to manage;
- More hardware means more space used, more cables and therefore higher chances of making mistakes;
- Lack of flexibility: the resources of a server are fixed and cannot easily be changed.
To sum up we can say that services run better and more securely when they are installed on different servers but using only one server is cheaper and easier to manage and maintain. Virtualization is a good compromise: it brings the pros of both solutions without the cons.
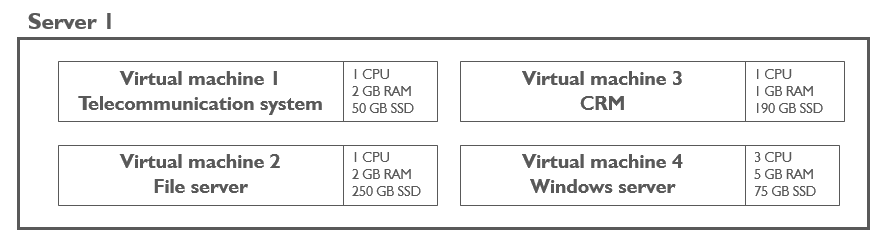
In a virtualized environment, the four computers are running within one server:
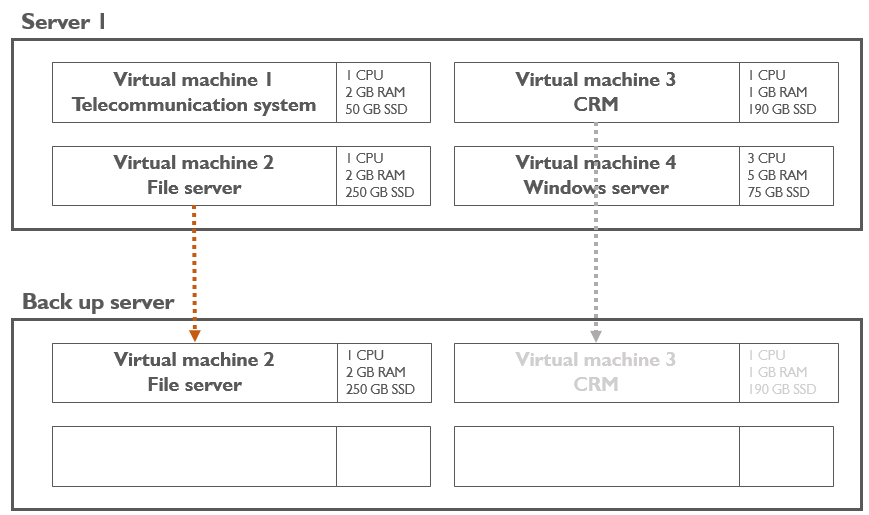
Virtualization means running different imaginary (virtual) computers on one real server: the programs do not see the difference between a real and a virtual computer. When the machines are virtualized it brings the same advantages as having one computer per machine, but on one server only: it is cheaper and needs less power. Virtual machines are also like boxes within a server. It is very easy to back them up and restore them on another server.
Finally a "virtual" machine is not real, which brings lots of flexibility: the user can define the perfect amount of resources needed to run the program and modify them later if needed. The user can also choose the best virtual hardware (network card, SSD, RAM, etc.) that composes the virtual machine in order to meet the exact needs of each program.
Virtualization brings the following advantages:
- Dedicated resources for each program - as if each program were running on a dedicated computer;
- Only one server: cheaper and easier to install and maintain;
- Easy backup: almost as simple as a copy & paste;
- Cheaper redundancy;
- Virtual: if a mistake is done in one machine, it's not a big deal, a new machine is only a few clicks away.
This is for all those reasons that we offer virtualization possibilities on the beroNet Appliance.